A new treatment for patients diagnosed with mesothelioma has recently been approved by the FDA and is now available at the West Cancer Center in Memphis, TN. This is the first center in the nation to use electric therapy treatment for these patients.
An Exciting New Treatment
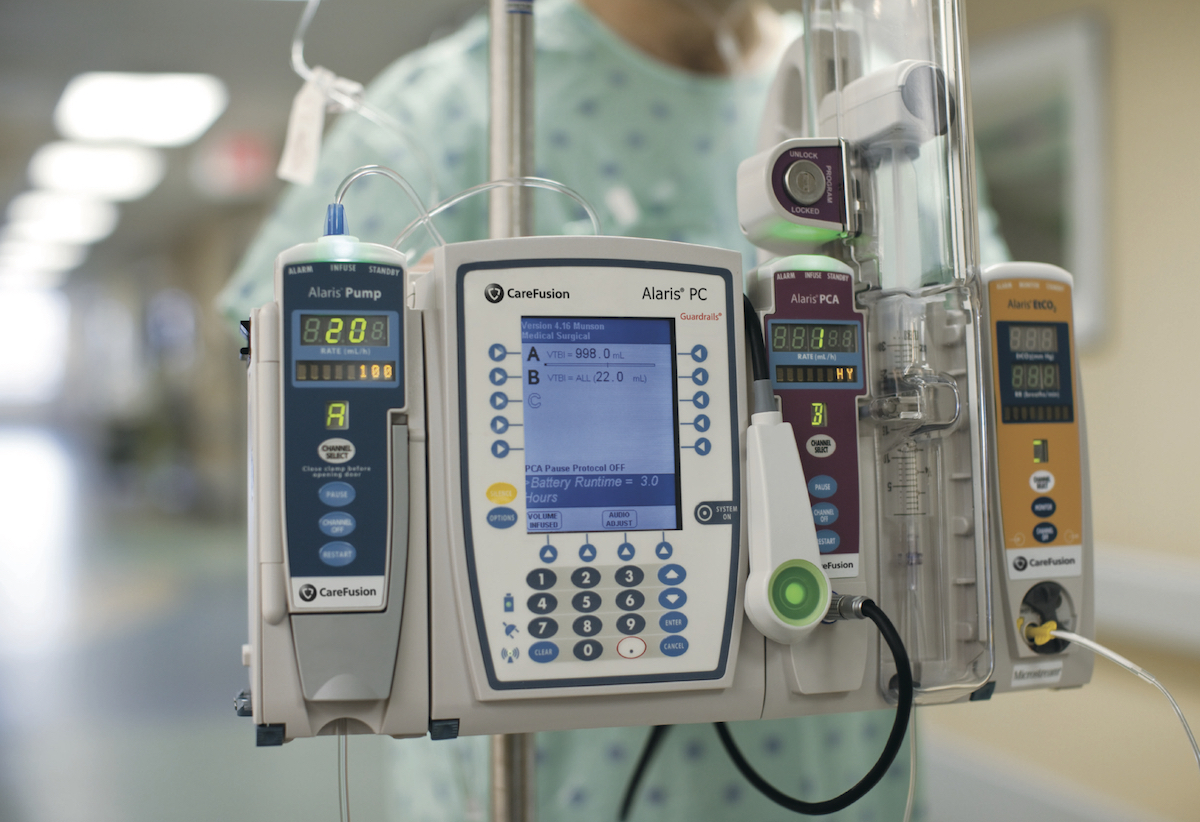
Electric therapy treatment works by sending electric fields into the body to target cancerous cells. The technician applies three pads to the front and back of the patient. Once the unit is turned on, electric fields are sent through the person’s body to disrupt the growth of the cancerous cells. At the same time, it leaves the healthy cells alone.
The new treatment promises to be popular because it’s not invasive. There are few side effects as well. The first patient has received the treatment, and they are wearing it for 18 hours each day. It is expected to have 97 percent control in the first year. If the patient uses the treatment along with chemotherapy, they may have a stable disease or positive response.
The device was first introduced in 2015 to treat brain tumors. It has since been used with ovarian and pancreatic cancer. It’s not being labeled as a cure, but it does help patients live longer. People diagnosed with mesothelioma normally have about two years life expectancy because this is an aggressive cancer. It’s rare, which makes research and treatment difficult.
Before the new treatment was approved, there were three options for treating mesothelioma, which included surgery, chemotherapy and radiation.
What is Mesothelioma?
Mesothelium is the tissue in the lining of your lungs, heart, stomach and other organs. Mesothelioma is a cancer of that tissue. It generally starts in the lungs, but it can begin in other organs as well. This condition has been linked to exposure to asbestos because the asbestos fibers get in the lungs when inhaled where they can’t disappear. Over time with constant exposure, more fibers get into the lungs. Symptoms of this disease often wait 20 or 30 years after exposure to show up. It starts with shortness of breath or pain in the chest. Fluid begins to accumulate, making it even more difficult to breathe.
Anyone who has been exposed to asbestos is at greater risk for developing mesothelioma. Even if you live with someone who works in the industry around asbestos can have an increased risk because they can inhale the fibers from that person’s clothing.
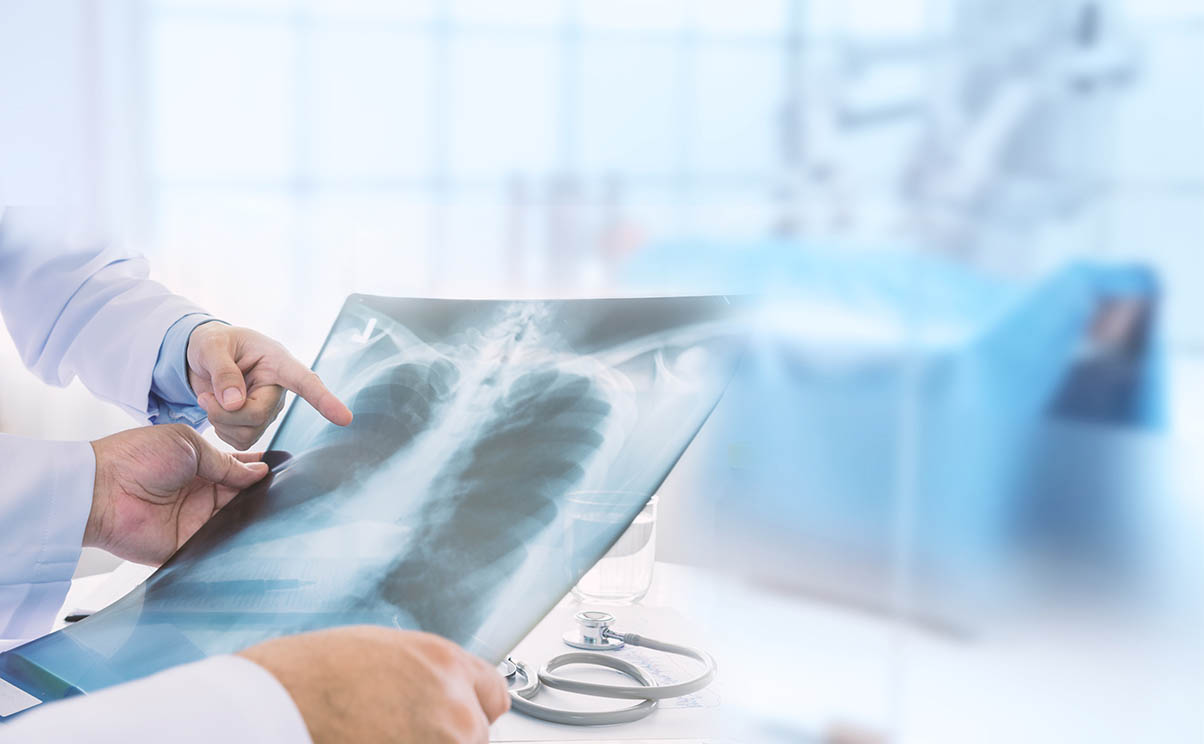
This type of cancer usually isn’t diagnosed until it’s advanced. The doctor will often order an X-ray of the chest or CT scan. If abnormalities are found, a biopsy may be ordered. After it has been analyzed, the results will tell if it is cancerous. Diagnosis could happen much more quickly if the person knows they were exposed to asbestos, but many people don’t think about these details of a job from 20 or 30 years ago.
Mesothelioma patients may find new hope with the treatment if it enhances the quality and quantity of their lives.